Around 10%-15% of healthcare professionals engage in substance abuse at some point in their careers.
Despite the high prevalence of substance abuse in the medical fraternity, it’s a challenging subject in conversations and mainstream media and is often shrouded in secrecy.
Not anymore. In this post, we’ll share important statistics for substance abuse among medical professionals.
KEY TAKEAWAYS
- Over 100,000 medical professionals struggle with abuse or addiction, with narcotics such as oxycodone and fentanyl being the most commonly involved substances.
- According to the Journal of Clinical Nursing, about 20% of nurses have problems with drugs or alcohol.
- A 2009 study revealed that 71% of physicians who undergo treatment and engage in continuous monitoring maintain sobriety, licensure, and employment after five years.
- Around 5.5% of medical professionals engage in illicit drug abuse—including marijuana use—as a means of relaxation after long shifts in healthcare settings.
- Actions against physician licenses for substance use are more common than those for psychological or physical impairment.
Substance Abuse by Type of Medical Professional
One in ten physicians experience drug or alcohol abuse at some point in their lives. Here are some substance abuse statistics according to the type of medical professional:
Anesthesiologists
- According to a 2009 study, over 40% of anesthesiologists in Physician Health Programs are there for intravenous drug use, while 10% are there for alcohol abuse.
- Anesthesiologists are particularly prone to opioid abuse due to easy access to potent opioids like fentanyl and sufentanil.
Surgeons
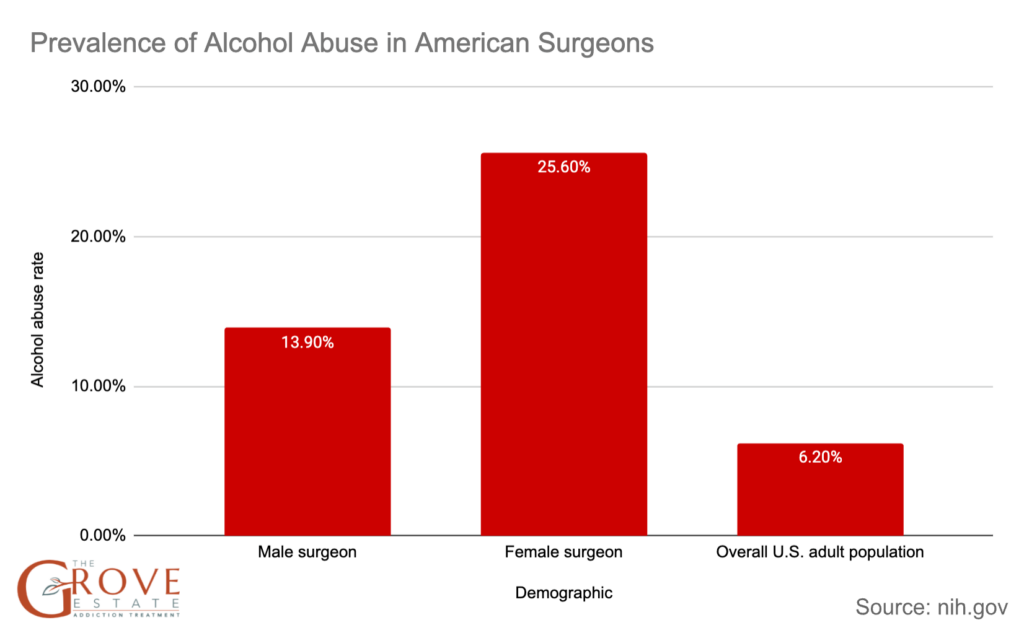
- In a 2012 study on U.S. surgeons, 25.6% of female surgeons and 13.9% of male surgeons were found to have alcohol abuse or dependence issues, compared to 6.2% of the overall U.S. adult population.
Psychiatrists
- In comparison to other medics, psychiatrists are particularly susceptible to stress, burnout, and even suicide. They are also more likely to abuse benzodiazepines compared to other medical professionals.
- A systematic review from 2004 found that the most common stressors for psychiatrists in the United States are as follows:
- Negative patient characteristics
- Intense responsibility
- Events leading to posttraumatic stress
- Administrative and staff-related issues
- Lengthy work hours
- Little to no positive feedback
- Low job satisfaction
- Lack of control
Emergency Medicine Physicians
- Emergency medicine physicians comprise only 3% of all physicians. However, they make up 7%-18% of those enrolled in Physician Health Programs for substance abuse management.
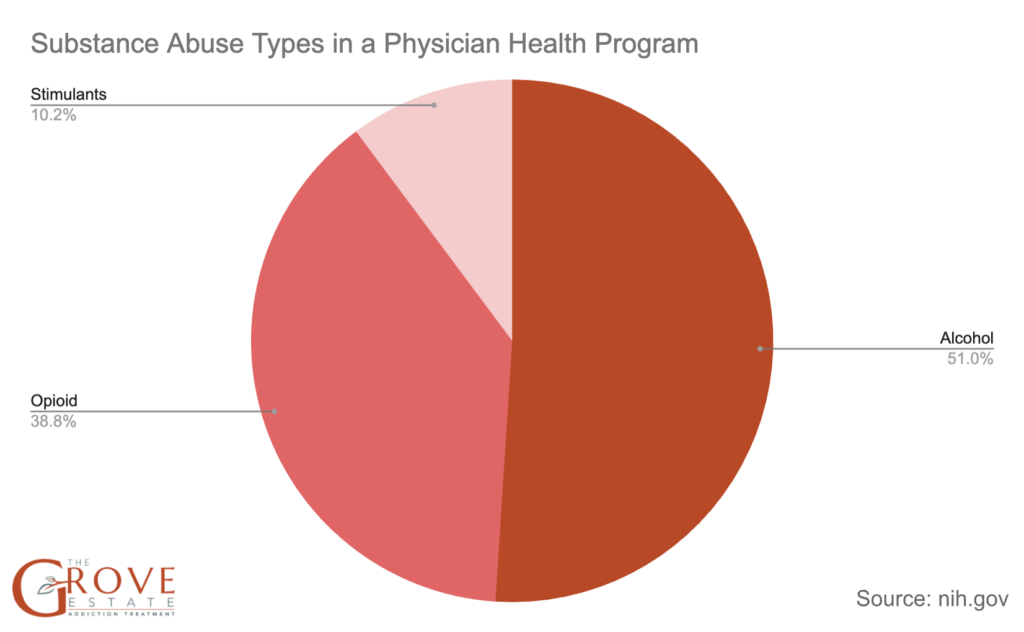
- According to one of the Physician Health Programs, nearly half of emergency medicine physicians were treated for alcohol abuse, 38% were treated for opioid addiction, and almost 10% were treated for stimulant use.
- Emergency medicine physicians face a burnout rate of 60%, the highest among physician specialties.
Factors Contributing to Substance Abuse Among Medical Professionals
Stress, exhaustion, long working hours, poor mental health, and toxic workplace culture are among the primary factors contributing to substance abuse by medical professionals. Here are some important numbers:
- Nearly one in three doctors exhibit symptoms of depression, with approximately 400 physicians dying by suicide annually.
- As compared to individuals in other occupations, healthcare workers exhibit higher rates of mood, anxiety disorders, and sleep disorders.
- In an American survey of 2,106 female physicians, nearly half were found to meet the criteria for mental illness. Many refrained from seeking treatment due to feelings of self-sufficiency, time constraints, fear of getting reported to a medical licensing board, and the perception of mental health diagnoses as being embarrassing or shameful.
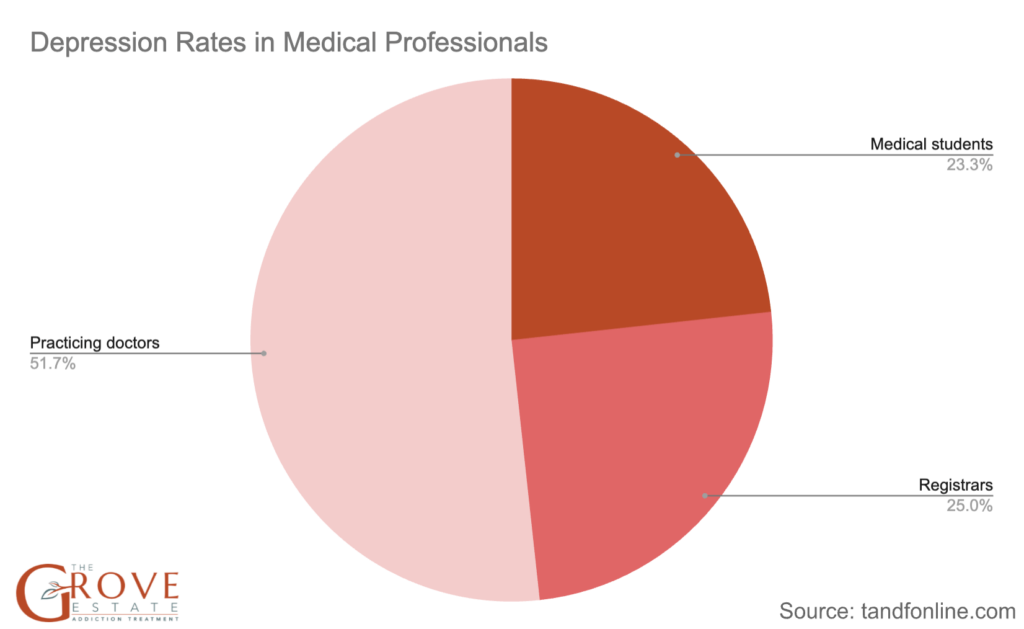
- Analyses indicate depression rates of 27% in medical students, 29% in registrars, and up to 60% in practicing doctors, varying across countries and specialties.
- A Cape Town study found moderate to severe depression in 30% of public primary healthcare doctors, whereas an Australian study reported depression diagnoses in 18% of medical students and 21% of doctors.
- Medical students, younger doctors, and women experience higher rates of psychological stress and mental health issues compared to older doctors and men.
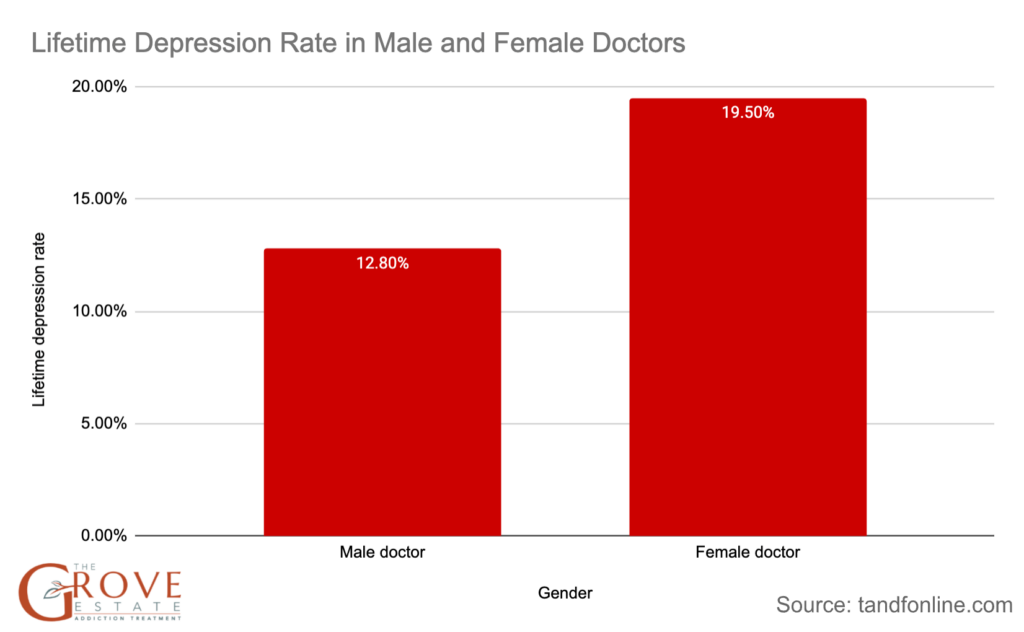
- In the United States, the prevalence of depression among doctors is similar to that of the general population, with lifetime prevalence rates of 12.8% for male doctors and 19.5% for female doctors.
- Depression incidence is generally similar across ethnic groups, except for lower rates among Asian women doctors.
- Evidence indicates a gradual rise in mental health symptoms among physicians over the past thirty years. One meta-analysis suggests that depression prevalence has increased by an average of 0.5% per year.
- Medical students and registrars/residents exhibit significantly higher prevalence rates of depression or depressive symptoms (15%-43.2%) compared to the general population.
Consequences of Substance Abuse Among Medical Professionals
Substance use can have severe consequences for medical practitioners, including an increased risk of criminal negligence and the possibility of losing their professional license. Here are some important numbers:
- Action due to substance abuse accounts for over three-fourths (76.3%) of all license actions.
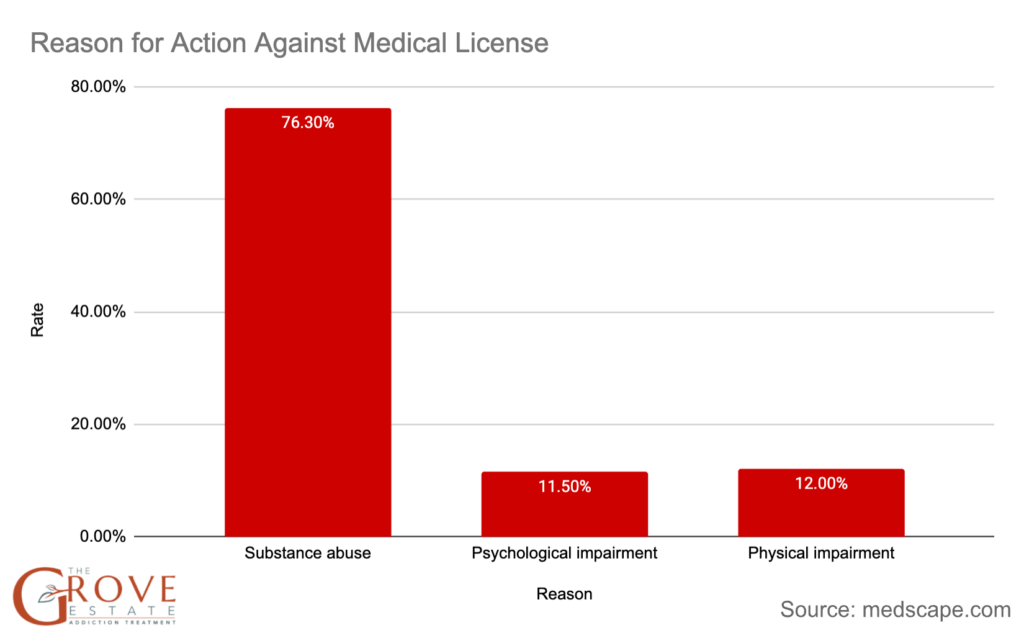
- Despite a sharp increase in 2011, actions related to substance use declined between 2004 and 2020.
Which Drugs Are Most Commonly Abused by Nurses?
Nurses tend to misuse prescription drugs, such as opioids and benzodiazepines. The American Nurses Association states that between 14% and 20% of all American nurses may be dependent on drugs or alcohol.
What Are the Causes of Substance Use Among Medical Students?
Substance use among medical students is caused by academic stress, peer pressure, and mental health issues.
Which Factors Contribute to Substance Abuse Among Medical Professionals?
Factors contributing to substance abuse among doctors include workplace stress, easy access to drugs, and personal vulnerabilities such as genetics or past trauma.
What Legal Consequences do Medical Professionals Face When Struggling with Substance Abuse?
When medical professionals struggle with substance abuse, they face significant legal consequences that can affect their licensure and ability to practice. Actions against their licenses, often resulting from impaired performance or misconduct linked to substance use, can lead to suspensions or revocation. This not only impacts their career but also their financial stability and professional reputation. Seeking timely help from programs like rehab for professionals can provide the necessary support to address substance abuse issues before they lead to legal repercussions.
Additionally, it’s essential to consider the broader implications of these legal actions on healthcare delivery. Patients’ safety and trust in the healthcare system can be compromised when professionals work while impaired. This is why it’s beneficial for medical professionals and their employers to be aware of and utilize Indiana mental health statistics to monitor and improve mental health support systems, thereby reducing the risk of substance abuse and its associated legal and professional consequences.
Data Sources
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19482236/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17242598/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22351913/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15143847/
- https://www.mentalhealthfirstaid.org/2017/06/medical-professionals-face-mental-health-issues/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5934846/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8849514/
- https://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/975200?form=fpf
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27796258/
- https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/20786190.2019.1610232
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9618683/

Share This Post



