In the realm of addiction treatment, the landscape is as varied as the individuals it seeks to help. Addiction, a complex and multifaceted condition, demands a diverse array of therapeutic approaches, each uniquely designed to address the intricate web of factors contributing to addictive behaviors. From cognitive-behavioral techniques that reshape thought patterns to holistic methods that nurture overall well-being, these therapies offer tailored pathways to recovery.
This article delves into the different types of therapy available for addiction treatment, highlighting how each method plays a crucial role in addressing not just the symptoms of addiction, but its root causes and the holistic recovery of the individual. Understanding these therapies provides insight into the nuanced and personalized nature of addiction treatment, a critical step for anyone on the journey to recovery or supporting someone through it.
What Are The Different Types Of Therapy For Addiction Treatment?

1. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is a form of psychotherapy that helps patients identify and challenge negative thought patterns and behaviors. In addiction treatment, CBT is particularly effective as it enables individuals to recognize triggers, develop coping strategies, and change the thought processes that contribute to their substance abuse. This therapy empowers individuals to take control of their actions and thoughts, leading to more positive and healthy behaviors.
2. Individual Therapy
Individual Therapy offers a personalized, one-on-one approach to addiction treatment, focusing on the unique needs and experiences of the individual. This form of therapy allows for a deep exploration of personal issues, traumas, and patterns contributing to addiction. It provides a safe and confidential environment where individuals can work through their challenges at their own pace, with the undivided attention and support of a therapist.
3. Family Therapy
Family Therapy involves integrating family members into the treatment process, recognizing that addiction impacts not just the individual but their entire family system. This therapy aims to heal relationships, improve communication, and build a supportive home environment. It educates family members about addiction, helps resolve conflicts, and fosters a deeper understanding among family members, which is crucial for the individual’s recovery journey.
4. Dialectical Behavioral Therapy (DBT)
Dialectical Behavioral Therapy (DBT) is a form of therapy that emphasizes the development of emotional regulation and mindfulness skills. In addiction treatment, DBT helps individuals manage intense emotions, reduce self-destructive behaviors, and improve relationships. It combines acceptance and change strategies, teaching patients how to live in the moment, cope healthily with stress, regulate emotions, and improve relationships with others.

5. Motivational Interviewing
Motivational Interviewing is a client-centered counseling style that encourages self-motivation to change harmful behaviors. Addiction treatment involves guided conversations where therapists help individuals explore their ambivalence about their addiction and elicit their motivations for change. This approach respects the individual’s autonomy and empowers them to take responsibility for their recovery, making it an effective tool for overcoming addiction.
6. Crisis Intervention
Crisis Intervention is a type of therapy that provides immediate support and strategies to individuals experiencing a psychological crisis. This approach is crucial in addiction treatment as it ensures the safety and stability of the individual in acute distress. It involves assessing the situation, de-escalating the crisis, and providing immediate support and resources. Crisis intervention aims to stabilize the individual’s emotional and mental state, offering a bridge to longer-term treatment solutions.
7. Couples Therapy
Couples Therapy in the context of addiction treatment focuses on addressing how addiction impacts both partners in a relationship. This therapy aims to foster a supportive and understanding environment, where both individuals can express their feelings, concerns, and experiences related to the addiction. It helps couples develop healthier communication patterns, rebuild trust, and work together towards recovery, recognizing that addiction is a shared challenge that requires joint effort and support.
8. Recreational Therapy
Recreational Therapy uses leisure activities as a therapeutic tool to improve physical, mental, and emotional well-being in individuals recovering from addiction. This therapy offers a fun and engaging way to develop new hobbies, build social skills, and enhance self-esteem. Activities can range from sports and games to arts and crafts, providing opportunities for individuals to discover new interests and ways to cope with stress, ultimately aiding in their overall recovery process.
9. Mindfulness Therapy
Mindfulness Therapy incorporates practices such as meditation, breathing exercises, and awareness techniques to help patients in addiction treatment stay grounded in the present moment. This approach teaches individuals to observe their thoughts and feelings without judgment, fostering a greater sense of calm and emotional regulation. By learning to be present and mindful, individuals can better manage cravings, reduce stress, and develop a deeper understanding of their behaviors and triggers, contributing to a more effective recovery process.
10. Aversion Therapy
Aversion Therapy is a behavioral treatment that creates negative associations with addictive substances to deter substance use. This method involves pairing the substance with an unpleasant stimulus, such as a bad taste or smell, leading to a conditioned aversion to the substance. The goal is to reduce the desire for the addictive substance by changing the individual’s response to it, thereby aiding in the recovery process.

11. Nutritional Counseling Therapy
Nutritional Counseling Therapy in addiction treatment focuses on improving overall health and wellness through dietary changes and nutritional education. Recognizing that substance abuse can lead to nutritional deficiencies and health issues, this therapy aims to restore physical health, enhance mood, and support the body’s recovery. By learning about healthy eating habits, individuals can better support their physical and mental well-being during the recovery process.
12. Trauma-Informed Therapy
Trauma-Informed Therapy is an approach that acknowledges the significant impact of trauma on an individual’s life and integrates this understanding into addiction treatment. This therapy recognizes that past trauma can be a root cause or contributing factor to substance abuse. It focuses on creating a safe and supportive environment where individuals can explore and process their traumatic experiences, helping to address the underlying issues that may be driving their addiction.
13. EMDR Therapy
EMDR Therapy (Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing) is a psychotherapy technique that utilizes eye movement to help process and reduce the impact of traumatic memories. In the context of addiction treatment, EMDR is used to address unresolved trauma that may be contributing to substance abuse. By reprocessing these traumatic memories, individuals can reduce their emotional distress, leading to improved mental health and aiding in their recovery journey.
14. Cognitive Processing Therapy
Cognitive Processing Therapy is a type of cognitive-behavioral therapy that helps patients learn how to modify and challenge unhelpful beliefs related to trauma. In addiction treatment, this therapy is particularly beneficial for individuals whose substance abuse is linked to traumatic experiences. It involves helping patients understand and reframe their thoughts about the trauma, reducing its ongoing impact, and enabling them to develop healthier coping mechanisms for both their trauma and addiction.
15. Cognitive Remediation Therapy
Cognitive Remediation Therapy is a treatment approach aimed at improving cognitive functions such as memory, attention, and problem-solving skills. In the context of addiction treatment, it addresses cognitive impairments that may have resulted from or contributed to substance abuse. By engaging in targeted cognitive exercises and activities, individuals can enhance their cognitive abilities, which is crucial for better decision-making, planning, and overall recovery success.
16. Electroconvulsive Therapy
Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT) is a medical treatment that involves inducing controlled seizures through electrical stimulation of the brain. While primarily used for severe depression and psychiatric conditions, ECT can also be beneficial in certain cases of addiction, particularly where co-occurring mental health disorders are present. It is considered for individuals who have not responded to other treatments, providing a potential reset for brain chemistry and improving mood and cognitive function.
17. Exposure Therapy
Exposure Therapy is a psychological treatment that encourages individuals to confront feared situations, objects, or memories in a controlled and safe environment. In addiction treatment, this approach is often used to help individuals face triggers and anxiety-inducing situations without resorting to substance use. Gradual exposure under therapeutic guidance reduces the power these triggers hold, enabling individuals to develop healthier coping mechanisms.
18. Habit Reversal Therapy
Habit Reversal Therapy is a behavioral therapy that teaches individuals skills to identify and change habits that are harmful or undesirable, such as substance use. This therapy involves becoming more aware of the triggers and consequences of the harmful habit, and then learning and practicing alternative behaviors in response to these triggers. It’s particularly effective in treating addictions by helping individuals replace substance use with healthier habits.

19. Hypnotherapy
Hypnotherapy utilizes hypnosis to alter an individual’s state of consciousness, making them more open to suggestions and guidance. In addiction treatment, hypnotherapy can help modify attitudes, perceptions, and behaviors related to substance abuse. It can be used to reduce cravings, enhance motivation for recovery, and address underlying psychological issues linked to the addiction, promoting healthier behavioral changes.
20. Nidotherapy
Nidotherapy is an environmental therapy that focuses on altering the individual’s environment to better suit their needs and reduce psychological distress. In addiction recovery, this can involve modifying living arrangements, workplace settings, or social situations to create a more supportive and less triggering environment. By adapting the environment to the individual’s requirements, ndiotherapy aims to reduce stress and create conditions more conducive to recovery.
21. Neurofeedback Therapy
Neurofeedback Therapy uses real-time displays of brain activity to teach individuals how to self-regulate their brain functions. In addiction treatment, this therapy can be particularly effective in helping patients gain control over their brainwave patterns, which can be disrupted by substance abuse. By learning to modify their brain activity, individuals can improve cognitive functions, reduce cravings, and enhance emotional regulation, contributing to more effective addiction recovery.
22. Schema Therapy
Schema Therapy explores and seeks to restructure negative patterns or themes in an individual’s life, often established in childhood and perpetuated into adulthood. In the context of addiction treatment, this therapy helps individuals identify and understand these deep-rooted schemas and how they influence current behaviors, including substance abuse. By addressing these underlying patterns, Schema Therapy aids in developing healthier coping mechanisms and life choices, leading to more fulfilling and addiction-free lives.
23. Psychodynamic Therapy
Psychodynamic Therapy focuses on increasing awareness of unconscious thoughts and behaviors, aiming to uncover deep-seated feelings and unresolved conflicts that may contribute to addiction. This therapy promotes insight and self-reflection, helping individuals understand the psychological roots of their substance abuse. Through this understanding, patients can work through these issues, leading to more conscious and healthier choices in their lives.
24. Rational Emotive Behavior Therapy (REBT)
Rational Emotive Behavior Therapy (REBT) challenges irrational beliefs and encourages the development of rational, logical thinking. In addiction treatment, REBT helps individuals identify and dispute irrational thoughts and beliefs that may lead to negative emotions and self-destructive behaviors, such as substance abuse. By replacing these thoughts with more rational and positive beliefs, individuals can develop healthier emotional responses and behaviors.
25. Gestalt Therapy
Gestalt Therapy emphasizes personal responsibility and focuses on the present moment and self-awareness. This approach encourages individuals in addiction treatment to become more aware of their thoughts, feelings, and actions in the here and now. By focusing on current experiences rather than past events or future anxieties, Gestalt Therapy helps individuals understand their needs and behaviors, leading to more self-aware and responsible choices in their recovery journey.

26. Systematic Desensitization Therapy
Systematic Desensitization Therapy is a technique that gradually exposes patients to anxiety-triggering stimuli in a controlled environment to reduce fear responses. In addiction treatment, this approach can be particularly effective for individuals whose substance use is linked to anxiety or phobias. By slowly and systematically confronting these triggers, patients learn to desensitize their reactions, reducing the need to use substances as a coping mechanism.
27. Holistic Therapy
Holistic Therapy in addiction treatment integrates various non-medical treatment methods to address the physical, emotional, mental, and spiritual needs of the whole person. This approach may include practices like yoga, meditation, acupuncture, and art therapy. By focusing on the entire well-being of the individual, Holistic Therapy aims to provide a more comprehensive and balanced approach to recovery, recognizing that lasting healing encompasses more than just addressing substance use.
28. Evidence-Based Therapy
Evidence-based therapy incorporates treatment methods that have been scientifically tested and validated for their effectiveness in addiction recovery. These therapies are based on rigorous research and clinical studies, ensuring that the approaches used are reliable and have a proven track record of success. By utilizing Evidence-Based Therapies, addiction treatment programs can offer the most effective and up-to-date methods for helping individuals overcome addiction and achieve long-term recovery.
29. Experiential Therapy
Experiential Therapy stands out as a dynamic approach that emphasizes action-based treatment methods to foster recovery from addiction. This form of therapy encourages individuals to engage in activities, tasks, or expressions that facilitate the exploration of complex emotions and unresolved issues in a tangible and interactive manner. Through direct experience and reflection, participants can confront emotions, patterns, and obstacles that contribute to their addiction.
30. Art Therapy
Art Therapy provides individuals with a medium to express themselves beyond words, tapping into the healing power of creativity. This approach facilitates self-exploration and expression, allowing individuals to process complex emotions and experiences related to addiction in a supportive, therapeutic setting.
31. Music Therapy
Music Therapy harnesses the emotional and connecting power of music to aid in the recovery process. Through participation in music creation, listening, and analysis, individuals can explore emotional states, improve mood, and develop coping mechanisms that support sobriety.
32. Equine Therapy
Equine Therapy involves interaction with horses to promote emotional growth and healing. This therapy emphasizes non-verbal communication, empathy, and trust-building, offering insights into personal behavior patterns and emotional states that are pivotal in the journey to recovery.
33. Adventure Therapy
Adventure Therapy takes the therapeutic process into the great outdoors, using nature-based activities to challenge, motivate, and build resilience. This approach supports the development of self-esteem, interpersonal skills, and problem-solving strategies, crucial components for a successful recovery.
34. Play Therapy
Play Therapy provides a dynamic way for individuals to explore feelings, address unresolved trauma, and enhance decision-making through the therapeutic use of play. It is particularly effective in creating a safe space for expression and learning in a less conventional, yet profoundly impactful manner.
35. Animal-assisted Therapy
Animal-assisted Therapy integrates trained animals, typically dogs or horses, into the therapeutic process to facilitate emotional healing. The presence of animals can reduce anxiety, enhance mood, and provide comfort, making it easier for individuals to open up and engage in the treatment process. Animal-assisted therapy is known for improving patient outcomes by fostering a calming, nurturing environment.
36. Harm Reduction
Harm Reduction focuses on minimizing the negative consequences associated with drug use, rather than on abstinence alone. This pragmatic approach promotes safety and health, supporting individuals wherever they are in their journey towards recovery.
How Effective Is Drug Addiction Therapy?
The efficacy of drug addiction therapy varies significantly based on individual factors, level of engagement in treatment, and the specific therapeutic approach. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) has been particularly effective, with research from the National Institute on Drug Abuse (2018) highlighting its lasting impact in reducing substance misuse. Patients tend to retain the skills learned in CBT long after the treatment has ended, indicating a positive, enduring influence on behavior.
Moreover, Contingency Management (CM) has shown promising results across various substance use disorders, including alcohol, stimulants, opioids, and marijuana. This method involves providing tangible rewards, such as vouchers or cash incentives, for maintaining abstinence and exhibiting positive behavioral changes. The National Institute on Drug Abuse (2018) supports this approach, noting its effectiveness in promoting recovery. Additionally, a clinical trial cited by Arch Gen Psychiatry (2005) revealed that incentive-based therapy could also enhance treatment retention, further validating its role in successful addiction treatment programs.
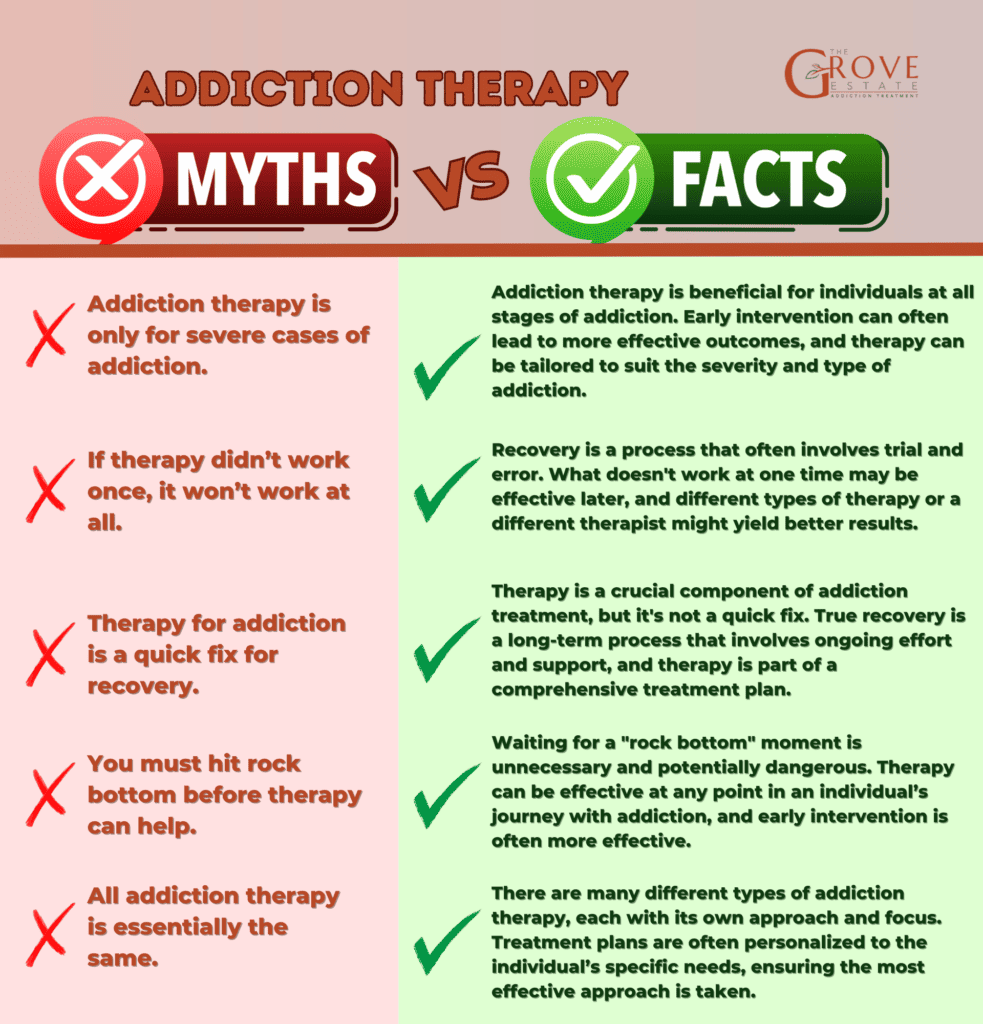
What Are Myths and Facts About Addiction Therapy?
- Myth: Addiction therapy is a one-size-fits-all solution.
- Fact: Addiction therapy is highly individualized. Different individuals may respond better to different types of therapy based on their personal history, the substance involved, and their psychological makeup.
- Myth: You have to hit rock bottom before therapy can help.
- Fact: Early intervention can be very effective in addiction therapy. Waiting for a crisis or a “rock bottom” moment is unnecessary and can be more damaging.
- Myth: Relapse after therapy means the treatment has failed.
- Fact: Relapse is often a part of the recovery process. It doesn’t mean failure but rather indicates a need for a revised or reinforced treatment approach.
- Myth: Addiction therapy is only about stopping drug use.
- Fact: Effective addiction therapy addresses the underlying issues contributing to the addiction, such as mental health disorders, trauma, and lifestyle factors, not just the cessation of drug use.
- Myth: Medications used in addiction treatment simply replace one addiction with another.
- Fact: Medications used in addiction treatment (like methadone or buprenorphine) are evidence-based treatments that can normalize brain chemistry, reduce cravings, and improve the success rates of treatment.
How Long Does Addiction Therapy Typically Last?
The duration of addiction therapy varies widely depending on individual needs, the severity of the addiction, and the type of therapy used. Short-term therapies may last a few weeks to a few months, while long-term therapies can extend to a year or more. Ongoing support, like group meetings or maintenance therapy, might continue indefinitely as part of a long-term recovery plan.
Can Therapy Alone Cure Addiction?
Therapy alone is often not a complete cure for addiction but is a critical component of a comprehensive treatment plan. It addresses the psychological aspects of addiction, but many individuals also benefit from medical interventions, lifestyle changes, and ongoing support. Recovery is typically more successful with a holistic approach that combines therapy with other treatment modalities.
Is Addiction Therapy Effective Without Medication?
Addiction therapy can be effective without medication, especially for individuals with mild to moderate addiction severity. Therapies like CBT, group therapy, and family therapy can provide significant benefits. However, for certain types of addiction or severe cases, combining therapy with medication-assisted treatment (MAT) can enhance effectiveness and support long-term recovery.
What is the Therapy with the Highest Success Rate for Addiction Treatment?
The success rate of addiction therapy varies, but evidence-based therapies like Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) and Motivational Interviewing often show high effectiveness. The success largely depends on the individual’s specific situation, including the nature of their addiction, personal history, and commitment to treatment. No single therapy is universally ‘best’; success is typically highest with a personalized approach that may combine different therapies.
What Determines the Type of Therapy Used in Addiction Treatment?
The type of therapy used in addiction treatment is determined by several factors, including the type of addiction, the individual’s mental and physical health, personal preferences, and treatment history. Therapists also consider factors like the presence of co-occurring disorders and the individual’s support system. A thorough assessment by a healthcare professional helps in tailoring the most appropriate therapy or combination of therapies for effective treatment.
Explore Your Path to Recovery
Embarking on the road to recovery is a courageous step, and understanding your options is vital. The Grove’s guide to addiction therapies is crafted to inform and inspire those seeking help, whether for themselves or a loved one. While we specialize in certain treatments, this resource serves as a comprehensive directory for a wide array of therapeutic possibilities. We encourage you to use this information as a starting point to find the therapy that aligns with your journey to wellness. Remember, the path to healing is unique for everyone, and knowledge is the first step towards finding the right help. Contact The Grove now for personalized assistance and compassionate support in your journey towards addiction recovery.














