Dimethyltryptamine, or DMT, is a naturally occurring psychedelic used in various traditional rituals and is now explored for potential therapeutic benefits, particularly for mental health issues like depression and PTSD. Though it shows promise in controlled environments, DMT also leads to psychological dependency, pushing users to seek repeated experiences. According to a study published by Columbia Mailman Health, the use of hallucinogens, including DMT, has seen a general increase, from 1.7% in 2002 to 2.2% in 2019, showing the need for careful management to prevent misuse
The effects of DMT addiction can vary widely but often include disturbances in psychological well-being, including anxiety, confusion, and disruptions in social or occupational functioning. Unlike other substances, where physical dependence is marked by withdrawal symptoms, DMT addiction’s primary concern is psychological.
Treatment focuses on psychological interventions. Counseling and therapy, particularly cognitive behavioral therapy, are effective in addressing the root causes of dependency and in developing healthier coping mechanisms. Additionally, support groups and retreats that focus on psychedelic recovery can provide communal support and guidance in overcoming the psychological grip of the substance.

What is DMT?
DMT (N, N-Dimethyltryptamine) is a potent hallucinogenic compound found in several plants native to Mexico, South America, and Asia, and can also be synthesized in laboratories. Classified as a Schedule I controlled substance by the DEA and banned by the FDA, DMT is recognized for its strong psychedelic effects and risk of abuse, with no accepted medical use in the U.S.
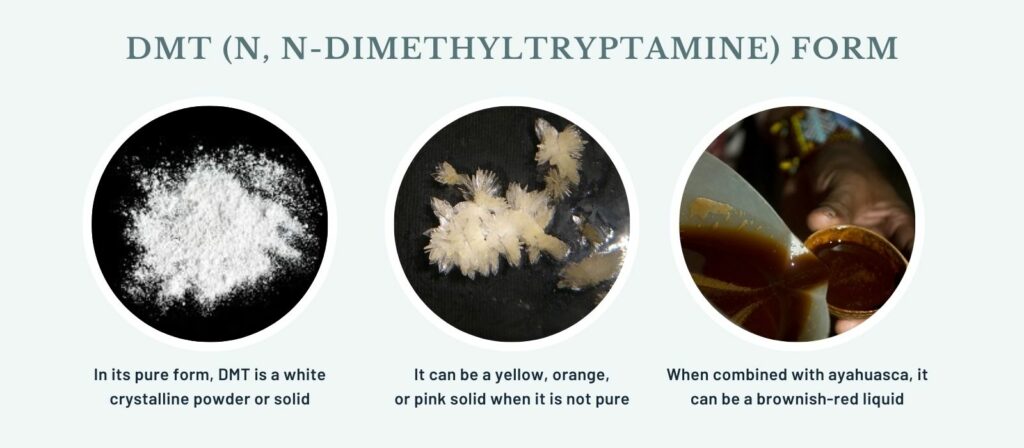
DMT is commonly ingested by smoking or vaporizing, and it’s also a key component of ayahuasca, a traditional South American brewed tea used in shamanistic rituals. Less commonly, it can be snorted. The method of intake influences the duration and intensity of the psychedelic experience, smoking or vaporizing DMT typically results in a short but intense experience, whereas ayahuasca can produce longer, more drawn-out effects.
According to a study published by the National Library of Medicine (NIH), DMT and related compounds are naturally present in the bodies of mammals, including humans. These substances interact with specific brain receptors and may act like neurotransmitters, important for transmitting brain signals. However, the exact role of these compounds in brain function remains unclear.

What are the Effects of DMT on the Body and Mind?
DMT (Dimethyltryptamine) exerts profound effects on both the mind and body, marking it as one of the most intense psychedelics known. This substance catapults users into a brief yet profound psychedelic experience characterized by vivid hallucinations and altered states of consciousness. Here is a list of the key effects of DMT on the body and mind:
Short-term Psychological and Physical Effects:
- Intense Hallucinations: Profound visual and auditory experiences, often perceived as otherworldly.
- Altered Perception: Shifts in the perception of time and reality.
- Emotional Impact: Rapid mood changes, potentially including feelings of euphoria or terror.
- Physical Sensations: Increased heart rate, higher blood pressure, and dilation of pupils.
- Nausea: Particularly common when consumed as part of ayahuasca.

Long-term Consequences of Habitual DMT Use:
- Psychological Dependency: Potential for non-physical addiction due to the desire to re-experience the psychedelic effects.
- Cognitive Effects: Possible changes in brain function or disruptions in thought processes.
- Hallucinogen Persisting Perception Disorder (HPPD): Ongoing visual disturbances and sensory distortions even after stopping the drug.
- Social Impact: Potential for impact on personal relationships and social responsibilities due to altered perception and behavior patterns.
Is DMT Addictive?
DMT has a low risk of physical dependency, it does not cause physical withdrawal symptoms, which points to minimal potential for physical addiction. However, the risk of psychological dependency exists because of the intense and profound experiences it delivers, which users may seek to repeat.
Addiction to DMT is more about psychological signs than physical ones. Indicators of a psychological dependency include:
- A persistent desire or unsuccessful efforts to cut down or control DMT use.
- Continued use despite social or interpersonal problems caused or exacerbated by the effects of DMT.
- Significant time spent in activities necessary to obtain, use, or recover from DMT’s effects.
If these behaviors are noticed, it could suggest a psychological dependency on DMT, similar to patterns seen with other psychedelics like LSD or psilocybin, which are known for their low physical addiction potential but significant psychological impact.

What are the Risks of DMT Use?
DMT (Dimethyltryptamine) use carries inherent risks, both psychologically and physiologically, that should be carefully considered due to the substance’s potent psychedelic effects. The psychological impacts of DMT are profound, affecting mental health in several ways. Users might experience “bad trips,” which are deeply distressing psychedelic episodes characterized by intense fear, anxiety, and disturbing hallucinations that have lasting effects on one’s psychological state.
Additionally, there is a risk of inducing psychosis, especially in those with pre-existing mental health issues or a susceptibility to psychotic disorders, presenting symptoms like delusions, paranoia, and disorganized thinking. On a long-term basis, regular DMT use leads to psychological dependency, with users becoming increasingly preoccupied with their psychedelic experiences. This obsession adversely affects personal relationships, job responsibilities, and overall well-being, as individuals may prioritize their drug experiences over other aspects of their life.
What are the Treatment Options for DMT Addiction?
DMT addiction treatment focuses on psychological rather than physical aspects, as DMT does not lead to physical dependency. Here are effective treatments:
- Psychological Therapies: Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) and psychotherapy are central to treating DMT addiction, helping individuals change behavior patterns and address underlying issues.
- Specialized Programs: Outpatient and inpatient programs offer structured therapy and support. Outpatient treatment allows individuals to maintain daily routines, while inpatient treatment provides intensive care in a controlled environment.
- Support Groups: Groups like Narcotics Anonymous provide peer support, sharing experiences and coping strategies.
- Integration Therapy and Education: Some centers offer integration therapy to help users understand and incorporate their psychedelic experiences into everyday life. Educational programs focus on the risks associated with DMT use and promote harm reduction strategies.

What is The Future of DMT in Addiction Treatment?
The potential for DMT (Dimethyltryptamine) in addiction treatment is increasingly acknowledged due to its interaction with specific brain receptors and its natural occurrence in the human body. Research indicates that DMT can act on these receptors in ways that might alter mood and perception, suggesting a possible role in addressing substance dependency issues. According to a study published in the Journal of Psychopharmacology by Garcia-Romeu et al. 2016, the therapeutic potential of psychedelics, including DMT, in treating addiction by facilitating profound, introspective experiences that could help individuals overcome dependencies on substances like alcohol and nicotine.
Clinical trials are underway to investigate the efficacy of psychedelics in addiction therapy. According to a 2017 study by Johnson et al., published by Johns Hopkins University, psychedelics lead to significant reductions in depression and anxiety, which are often comorbid with substance abuse. The therapeutic effects are thought to come from psychedelics’ ability to disrupt negative thought patterns and provide transformative experiences that give individuals new perspectives on their behaviors and motivations.
What are some slang names for DMT?
Common nicknames for DMT include Dimitri, which is a personification of the chemical name. It’s also called Fantasia, suggestive of its hallucinogenic properties. Another term used is Businessman’s Trip or Businessman’s Special, reflecting the short duration of its effects compared to other psychedelics. These names are commonly used in recreational settings to describe the unique and intense experience provided by DMT.
How is DMT different from other hallucinogens?
DMT stands out among hallucinogens primarily because of its intensity and the speed of its effects. It produces a rapid, very profound psychedelic experience that typically lasts about 30 minutes, much shorter than LSD or psilocybin trips. Additionally, DMT is structurally similar to serotonin and targets specific serotonin receptors intensely, which can lead to very vivid and life-like hallucinations.
Why is DMT illegal in most countries?
DMT is classified as a Schedule I drug under the United Nations 1971 Convention on Psychotropic Substances, which means it is considered to have a high potential for abuse, no recognized medical use, and a lack of accepted safety for use under medical supervision. As a result, DMT is illegal in most countries to control its non-medical use and potential health risks.
Can you die from taking DMT?
Deaths directly attributed to DMT toxicity are extremely rare. The primary risks of DMT are psychological rather than physiological, including potential for triggering or exacerbating mental health issues like psychosis. However, risky behaviors resulting from impaired judgment during intense trips, or potential harm from impure substances mixed with DMT, could pose significant risks.
How does DMT interact with the brain?
DMT acts on several neurotransmitter systems in the brain, primarily targeting serotonin receptors. This interaction is responsible for its potent psychedelic effects. According to studies published by the National Library of Medicine, DMT binds to these receptors and significantly alters the electrical and chemical activity of the brain, leading to its intense hallucinogenic effects. The profound changes in brain activity are believed to be behind both the therapeutic potentials and the risks of using DMT.
The understanding of how DMT affects the brain is crucial for developing safe therapeutic applications and for informing users about the risks associated with its use. This is particularly important for developing treatment plans that incorporate holistic approaches like exercise and nutrition, which can help mitigate some of the psychological risks associated with DMT use by strengthening overall mental and physical health.
How does DMT addiction differ from LSD addiction?
DMT addiction primarily involves a psychological dependency, with users often seeking to repeat the intense and unique experiences it provides. Unlike substances that cause physical dependency, DMT does not typically lead to physical withdrawal symptoms, making its addiction profile primarily psychological. This type of dependency can lead to significant disruptions in personal and professional life as individuals may become preoccupied with obtaining and using the substance.
In comparison, LSD addiction also manifests mainly as a psychological dependency, but the nature of LSD’s effects—longer-lasting and less intense per dose than DMT—creates different patterns of use and risks. Both substances require careful consideration of their psychological impacts, but the shorter, more intense trips associated with DMT can lead to a quicker onset of psychological dependency among its users. Understanding these differences is crucial for developing effective treatment strategies that address the specific needs of individuals addicted to these substances.

Share This Post



